基于 Next.js 16.0.1 官方文档整理
目录
什么是 Cache Components 核心工作原理 使用 Suspense 边界 使用 use cache 启用 Cache Components 从旧版本迁移 实战示例 最佳实践 和 Next-intl 结合 常见错误与解决方案 FAQ 参考资料
这边文档主要是 AI 总结+我补充实际遇到的问题,大部分是 AI 写的。
注意,文档里不包含use cache: private的内容,在写的时候本来官方文档里说依赖unstable_prefetch,但是后来一看这个内容又被移除了,不知道后续会不会再改,先不写了,以官方文档为准。API Reference > Directives > use cache: private
注意,现在的 16.0 还在不断变化中,还是等 16.1,16.2 再用吧。这东西太不稳了。
Cache components除了方便的 PPR+显式缓存,另外一个就是在框架层面(主要是 dev 和构建的时候),防止用户写出动态内容卡住整个页面加载的事,这在之前很容易写出来,网上也有很多批评的文章和视频,一看连loading.tsx和Suspense都不会用。😂
什么是 Cache Components Cache Components 是 Next.js 16 中一种新的渲染和缓存方法,通过 Partial Prerendering (PPR) 提供细粒度的缓存控制,同时确保出色的用户体验。
核心关系 1 Cache Components = PPR + use cache
PPR 提供静态外壳和流式传输基础设施use cache
解决的问题 在开发动态应用时,你需要在两种方式之间权衡:
❌ 完全静态页面 :加载快,但无法显示个性化或实时数据
❌ 完全动态页面 :可显示最新数据,但每次请求都需要渲染所有内容,导致初始加载慢
✅ Cache Components 的解决方案 :
启用 Cache Components 后,Next.js 将所有路由默认视为动态 。每个请求都使用最新可用数据渲染。但大多数页面由静态和动态部分组成,并非所有动态数据都需要在每次请求时从源获取。
Cache Components 允许你标记数据,甚至将 UI 的部分标记为可缓存,这会将它们与页面的静态部分一起包含在预渲染阶段中。
工作流程 当用户访问路由时:
服务器发送静态外壳 :包含缓存内容,确保快速初始加载动态部分显示 fallback :包裹在 Suspense 边界中的动态部分在外壳中显示 fallback UI动态内容流式传输 :只有动态部分渲染以替换其 fallback,并行流式传输缓存的动态数据包含在外壳中 :通过 use cache 缓存的原本动态的数据可以包含在初始外壳中
官方视频 : Why PPR and how it works (10 分钟)
核心工作原理 Cache Components 提供三个关键工具来控制渲染:
1. Suspense for Runtime Data(运行时数据) 某些数据仅在实际用户发出请求时在运行时可用。
运行时 API 包括 :
使用方法 :将使用这些 API 的组件包裹在 Suspense 边界中,以便页面的其余部分可以预渲染为静态外壳。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import { Suspense } from "react" ;import { cookies } from "next/headers" ;export default function Page ( return ( <div > {/* 静态部分 - 立即显示 */} <header > My App</header > {/* 动态部分 - 需要 Suspense */} <Suspense fallback ={ <div > Loading user...</div > }> <UserInfo /> </Suspense > </div > ); } async function UserInfo ( const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; const user = await db.users .findUnique ({ where : { id : userId } }); return <div > Welcome, {user.name}</div > }
2. Suspense for Dynamic Data(动态数据) 动态数据如 fetch 调用或数据库查询可能在请求之间发生变化,但不是用户特定的。
动态数据模式包括 :
使用方法 :将使用这些的组件包裹在 Suspense 边界中以启用流式传输。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 import { Suspense } from "react" ;export default function Page ( return ( <div > <h1 > Products</h1 > <Suspense fallback ={ <div > Loading products...</div > }> <ProductList /> </Suspense > </div > ); } async function ProductList ( const products = await db.products .findMany (); return ( <ul > {products.map((p) => ( <li key ={p.id} > {p.name}</li > ))} </ul > ); }
3. Cached Data with use cache(缓存数据) 将 use cache 添加到任何 Server Component 以使其缓存并包含在预渲染的外壳中。
限制 :
❌ 不能在缓存组件内使用运行时 API(cookies、headers 等)
✅ 可以标记工具函数为 use cache 并从 Server Components 调用
1 2 3 4 5 export async function getProducts ( "use cache" ; const data = await db.query ("SELECT * FROM products" ); return data; }
使用 Suspense 边界 React Suspense 边界让你定义当它包裹动态或运行时数据时使用什么 fallback UI。
基本用法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import { Suspense } from "react" ;export default function Page ( return ( <> <h1 > 这会被预渲染</h1 > <Suspense fallback ={ <Skeleton /> }> <DynamicContent /> </Suspense > </> ); } async function DynamicContent ( const res = await fetch ("http://api.cms.com/posts" ); const { posts } = await res.json (); return <div > {/* 渲染文章 */}</div > }
工作原理 :
边界外的内容(包括 fallback UI)被预渲染为静态外壳
边界内的内容在准备好时流式传输
在构建时,Next.js 预渲染静态内容和 fallback UI,而动态内容被推迟到用户请求路由时。
注意 :将组件包裹在 Suspense 中不会使其动态;你的 API 使用决定了这一点。Suspense 作为封装动态内容和启用流式传输的边界。
缺少 Suspense 边界时的错误 Cache Components 强制要求动态代码必须包裹在 Suspense 边界中。如果忘记,你会看到错误:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Uncached data was accessed outside of <Suspense> This delays the entire page from rendering, resulting in a slow user experience. Next.js uses this error to ensure your app loads instantly on every navigation. To fix this, you can either: - Wrap the component in a <Suspense> boundary - Move the asynchronous await into a Cache Component("use cache")
修复方法 :
添加 Suspense 边界 (推荐)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 export default function Page ( return ( <Suspense fallback ={ <Loading /> }> <DynamicComponent /> </Suspense > ); }
使用 use cache 缓存工作
1 2 3 4 5 async function DynamicComponent ( "use cache" ; const data = await fetch ("..." ); return <div > {data}</div > }
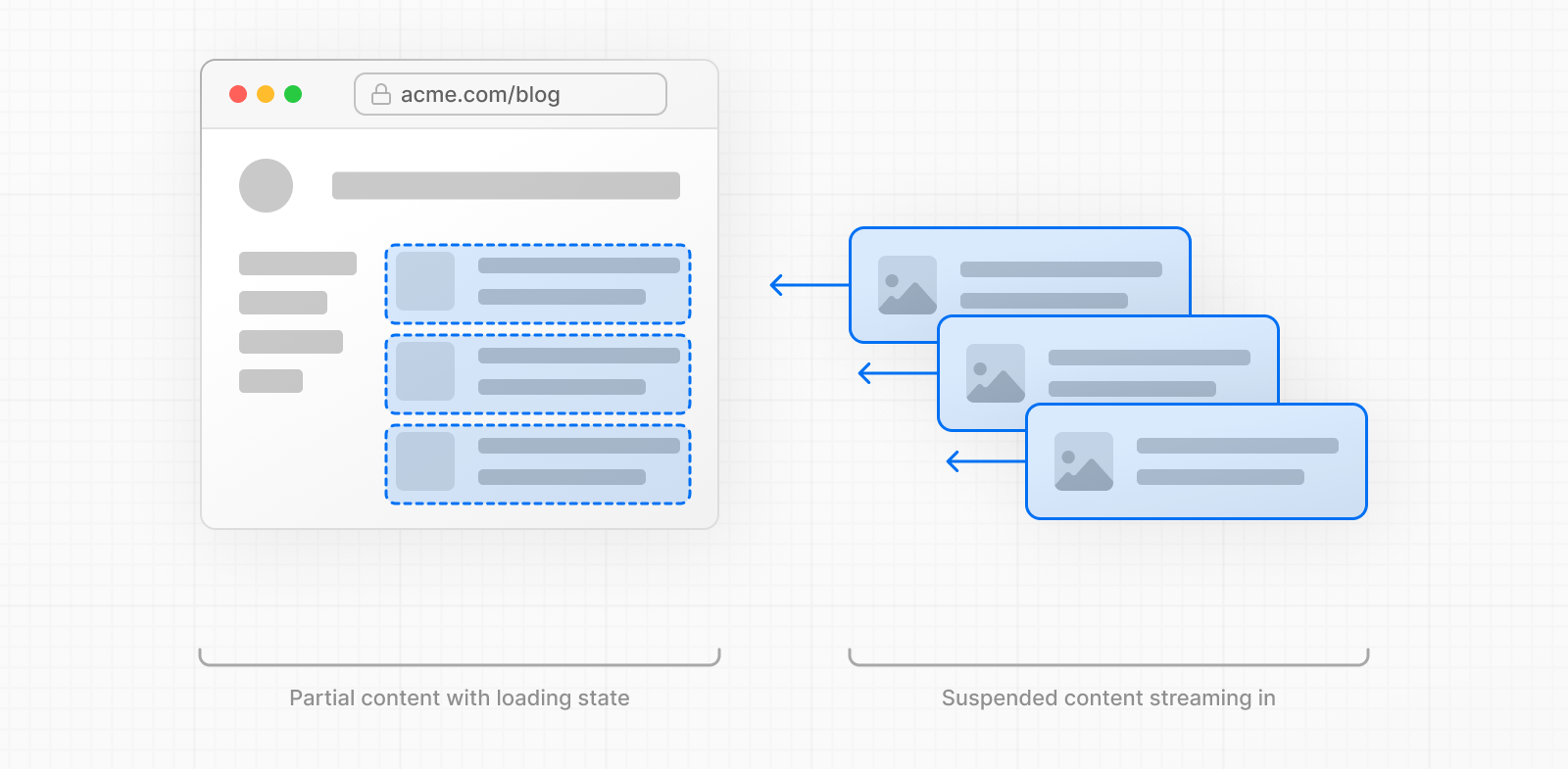
流式传输工作原理 流式传输将路由分割成块,并在准备好时逐步流式传输到客户端。这允许用户在整个内容完成渲染之前立即看到页面的部分内容。
通过部分预渲染,初始 UI 可以立即发送到浏览器,而动态部分则在渲染时流式传输。这减少了 UI 显示时间,并可能减少总请求时间。
为了减少网络开销,完整响应(包括静态 HTML 和流式动态部分)在单个 HTTP 请求 中发送。这避免了额外的往返,并提高了初始加载和整体性能。
使用 use cache 虽然 Suspense 边界管理动态内容,但 use cache
基本用法 将 use cache 添加到页面、组件或异步函数,并使用 cacheLife
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import { cacheLife } from "next/cache" ;export default async function Page ( "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); const data = await fetch ("https://api.example.com/data" ); return <div > {/* 渲染数据 */}</div > }
cacheLife 预定义配置
Profile
Use Case
stale
revalidate
expire
'default'Standard content
5 minutes
15 minutes
1 year
'seconds'Real-time data
30 seconds
1 second
1 minute
'minutes'Frequently updated content
5 minutes
1 minute
1 hour
'hours'Content updated multiple times per day
5 minutes
1 hour
1 day
'days'Content updated daily
5 minutes
1 day
1 week
'weeks'Content updated weekly
5 minutes
1 week
30 days
'max'Stable content that rarely changes
5 minutes
30 days
1 year
expire 要大于 stale,stale 不要小于 30s(不然缓存没意义)。
自定义配置 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import { cacheLife } from "next/cache" ;async function CustomCache ( "use cache" ; cacheLife ({ stale : 60 , revalidate : 300 , expire : 3600 , }); const data = await fetch ("https://api.example.com/data" ); return data; }
构建时与运行时行为 use cache at build time(构建时) 当在 layout 或 page 顶部使用 use cache 时,路由段会被预渲染,允许之后重新验证。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "use cache" ;export default async function ProductsPage ( cacheLife ("hours" ); const products = await fetch ("https://api.example.com/products" ).then ((res ) => res.json () ); return <div > {/* 渲染产品 */}</div > }
特点 :
✅ 路由段在构建时预渲染
✅ 可以后续 revalidated
❌ 不能与运行时数据一起使用 (cookies、headers)
重要限制 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 "use cache" ;export default async function Page ( const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; return <div > {userId}</div > }
注意 :如果需要缓存依赖 cookies、headers 或 search params 的内容,请使用 'use cache: private' 代替。
use cache at runtime(运行时) 当应用运行时,use cache 在服务器和客户端的行为:
服务器端 :
单个组件或函数的缓存条目会缓存在内存中
多个请求可以共享这些缓存条目
客户端 :
从服务器缓存返回的任何内容会存储在浏览器内存中
持续整个会话或直到重新验证
页面刷新或导航离开会清除缓存
示例 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 async function getCachedProducts ( "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); return await db.products .findMany (); } export default async function Page ( const products = await getCachedProducts (); return <div > {/* 渲染产品 */}</div > }
缓存生命周期 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 构建时: ┌─────────────────────────────────────┐ │ 1. 预渲染路由段 │ 2. 生成静态 HTML │ 3. 缓存结果供后续请求使用 └─────────────────────────────────────┘ 运行时(服务器): ┌─────────────────────────────────────┐ │ 请求 1 → 执行函数 → 缓存结果(内存) │ 请求 2 → 命中缓存 → 返回缓存结果 │ 请求 3 → 命中缓存 → 返回缓存结果 │ ...直到重新验证或过期 └─────────────────────────────────────┘ 运行时(客户端): ┌─────────────────────────────────────┐ │ 1. 接收服务器缓存的数据 │ 2. 存储在浏览器内存 │ 3. 导航时复用(同一会话) │ 4. session过期或者revalidated → 清除 └─────────────────────────────────────┘
使用限制 1. 参数必须可序列化 与 Server Actions 类似,缓存函数的参数必须是可序列化的。这意味着你可以传递原始类型、普通对象和数组,但不能传递类实例、函数或其他复杂类型。
2. 可接受但不能内省不可序列化的值 你可以接受不可序列化的值作为参数,只要你不内省它们。但是,你可以返回它们。这允许像缓存组件接受 Server 或 Client Components 作为 children 的模式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import { ReactNode } from "react" ;export async function CachedWrapper ({ children }: { children: ReactNode } ) { "use cache" ; return ( <div className ="wrapper" > <header > Cached Header</header > {children} </div > ); }
关键点 :不可序列化的参数(如 JSX、函数)不会成为缓存键的一部分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 async function getCached ( id : number , children : ReactNode , callback : () => void "use cache" ; return { id, content : <div > {children}</div > } const result1 = await getCached (1 , <div > A</div > () => {});const result2 = await getCached (1 , <div > B</div > () => {});
3. 避免传递动态输入 除非你避免内省它们,否则不能将动态或运行时数据传递到 use cache 函数中。传递来自 cookies()、headers() 或其他运行时 API 的值作为参数将导致错误,因为无法在预渲染时确定缓存键。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 async function BadExample ( "use cache" ; const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; return <div > {userId}</div > } async function GoodExample ( const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; return <div > {userId}</div > }
标记和重新验证 使用 cacheTagupdateTagrevalidateTag
使用 updateTag(立即更新) 当你需要在同一请求中过期并立即刷新缓存数据时使用 updateTag:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "use server" ;import { cacheTag, updateTag } from "next/cache" ;export async function getCart ( "use cache" ; cacheTag ("cart" ); } export async function updateCart (itemId : string "use server" ; updateTag ("cart" ); }
使用场景 :
✅ 需要用户立即看到更新(如购物车)
✅ Read-your-own-writes 模式
✅ Server Actions 专用
使用 revalidateTag(后台重新验证) 当你想要仅使正确标记的缓存条目失效并采用 stale-while-revalidate 行为时使用 revalidateTag。这对于可以容忍最终一致性的静态内容是理想的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 "use server" ;import { cacheTag, revalidateTag } from "next/cache" ;export async function getPosts ( "use cache" ; cacheTag ("posts" ); } export async function createPost (post : FormData "use server" ; revalidateTag ("posts" , "max" ); }
使用场景 :
✅ 可以容忍短暂过期数据(如博客文章、CMS 内容)
✅ 避免”惊群效应”(多个请求同时触发数据重新生成)
✅ Server Actions + Route Handlers
为什么推荐使用 'max' 配置 :
revalidateTag(tag, 'max') 使用 Stale-While-Revalidate (SWR) 策略:
调用 revalidateTag
缓存标记为 “stale”(过期但仍可用)
下一个请求:
✅ 立即返回过期缓存(快速响应)
🔄 同时后台触发重新验证
再下一个请求:
优势 :
用户不会遇到”等待数据重新生成”的延迟
避免高流量时的并发数据库查询
平滑的数据更新过渡
启用 Cache Components 在 next.config.ts 中添加 cacheComponents
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import type { NextConfig } from "next" ;const nextConfig : NextConfig = { cacheComponents : true , }; export default nextConfig;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 const nextConfig = { cacheComponents : true , }; module .exports = nextConfig;
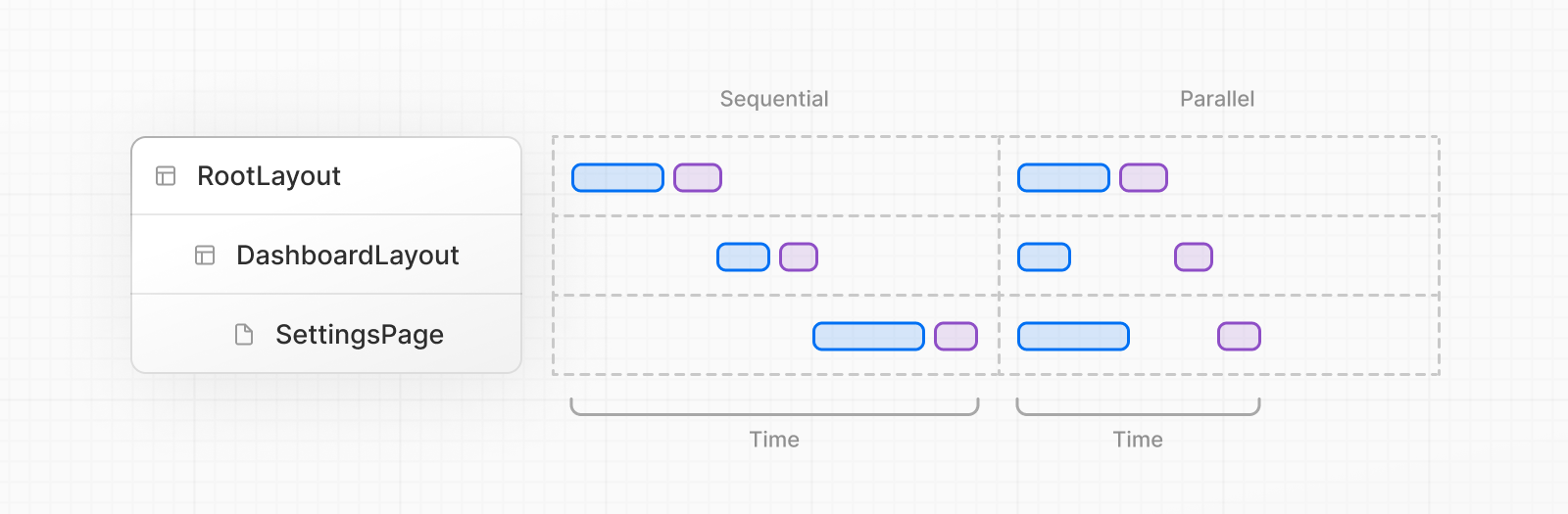
Navigation with Cache Components 当启用 cacheComponents<Activity>
工作方式:
状态保留 :导航离开时不卸载前一个路由,而是设置 Activity 模式为 "hidden"导航回退 :导航回来时,前一个路由及其状态完整保留效果清理 :路由隐藏时清理效果,再次可见时重新创建
好处 :通过在用户前后导航时维护 UI 状态(表单输入、展开的部分)来改善导航体验。
注意 :Next.js 使用启发式方法保持几个最近访问的路由为 "hidden"
从旧版本迁移 启用 Cache Components 后,几个 Route Segment Config 选项不再需要或不受支持。以下是变化和迁移方法:
1. dynamic = "force-dynamic" 不再需要 。启用 Cache Components 后,所有页面默认是动态的,因此此配置不必要。
1 2 3 4 5 6 export const dynamic = "force-dynamic" ;export default function Page ( return <div > ...</div > }
1 2 3 4 export default function Page ( return <div > ...</div > }
2. dynamic = "force-static" 用 use cache 替代 。你必须为关联路由的每个 Layout 和 Page 添加 use cache。
16.0.1 版本实际测试发现cache-control变成no-store了,关闭 cacheComponent 会出现 s-maxage 和 swr,行为不一致。
注意 :force-static 之前允许使用运行时 API 如 cookies(),但现在不再支持。如果你添加 use cache 并看到与运行时数据相关的错误,你必须移除运行时 API 的使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 export const dynamic = "force-static" ;export default async function Page ( const data = await fetch ("https://api.example.com/data" ); return <div > ...</div > }
1 2 3 4 5 6 export default async function Page ( "use cache" ; const data = await fetch ("https://api.example.com/data" ); return <div > ...</div > }
3. revalidate 用 cacheLife 替代 。使用 cacheLife 函数定义缓存持续时间,而不是路由段配置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 export const revalidate = 3600 ; export default async function Page ( return <div > ...</div > }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import { cacheLife } from "next/cache" ;export default async function Page ( "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); return <div > ...</div > }
4. fetchCache 不再需要 。使用 use cache 时,缓存范围内的所有数据获取都会自动缓存,使 fetchCache 不必要。
1 2 export const fetchCache = "force-cache" ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 export default async function Page ( "use cache" ; return <div > ...</div > }
5. runtime = 'edge' 不支持 。Cache Components 需要 Node.js 运行时,使用 Edge Runtime 会抛出错误。
实战示例 示例 1: 动态 API 使用 当访问运行时 API 如 cookies() 时,Next.js 只会预渲染此组件上方的 fallback UI。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 import { cookies } from "next/headers" ;export async function User ( const session = (await cookies ()).get ("session" )?.value ; return <div > User: {session}</div > }
页面组件 (需要 Suspense):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import { Suspense } from "react" ;import { User } from "./user" ;export default function Page ( return ( <section > <h1 > 这会被预渲染</h1 > <Suspense fallback ={ <div > Loading user...</div > }> <User /> </Suspense > </section > ); }
示例 2: 传递动态 Props 组件只有在访问值时才选择动态渲染。例如,如果你从 <Page /> 组件读取 searchParams,你可以将此值作为 prop 转发到另一个组件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import { Table , TableSkeleton } from "./table" ;import { Suspense } from "react" ;export default function Page ({ searchParams, }: { searchParams: Promise <{ sort: string }>; } ) { return ( <section > <h1 > 这会被预渲染</h1 > <Suspense fallback ={ <TableSkeleton /> }> <Table searchParams ={searchParams.then((search) => search.sort)} /> </Suspense > </section > ); }
Table 组件 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 export async function Table ({ sortPromise }: { sortPromise: Promise <string > } ) { const sort = (await sortPromise) === "true" ; return <div > {/* 渲染表格 */}</div > }
示例 3: Route Handlers with Cache Components GET Route Handlers 遵循与应用中正常 UI 路由相同的模型。它们默认是动态的,可以在确定性时预渲染,你可以使用 use cache 在缓存响应中包含更多动态数据。
动态示例 (每次请求返回不同数字):
1 2 3 4 5 6 export async function GET ( return Response .json ({ randomNumber : Math .random (), }); }
静态示例 (在构建时预渲染):
1 2 3 4 5 6 export async function GET ( return Response .json ({ projectName : "Next.js" , }); }
缓存动态数据示例 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import { cacheLife } from "next/cache" ;export async function GET ( const products = await getProducts (); return Response .json (products); } async function getProducts ( "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); return await db.query ("SELECT * FROM products" ); }
注意 :
use cache 不能直接在 Route Handler 主体中使用;提取到辅助函数缓存响应根据 cacheLife 在新请求到达时重新验证
使用运行时 API 如 cookies() 或 headers(),或调用 connection(),始终推迟到请求时(无预渲染)
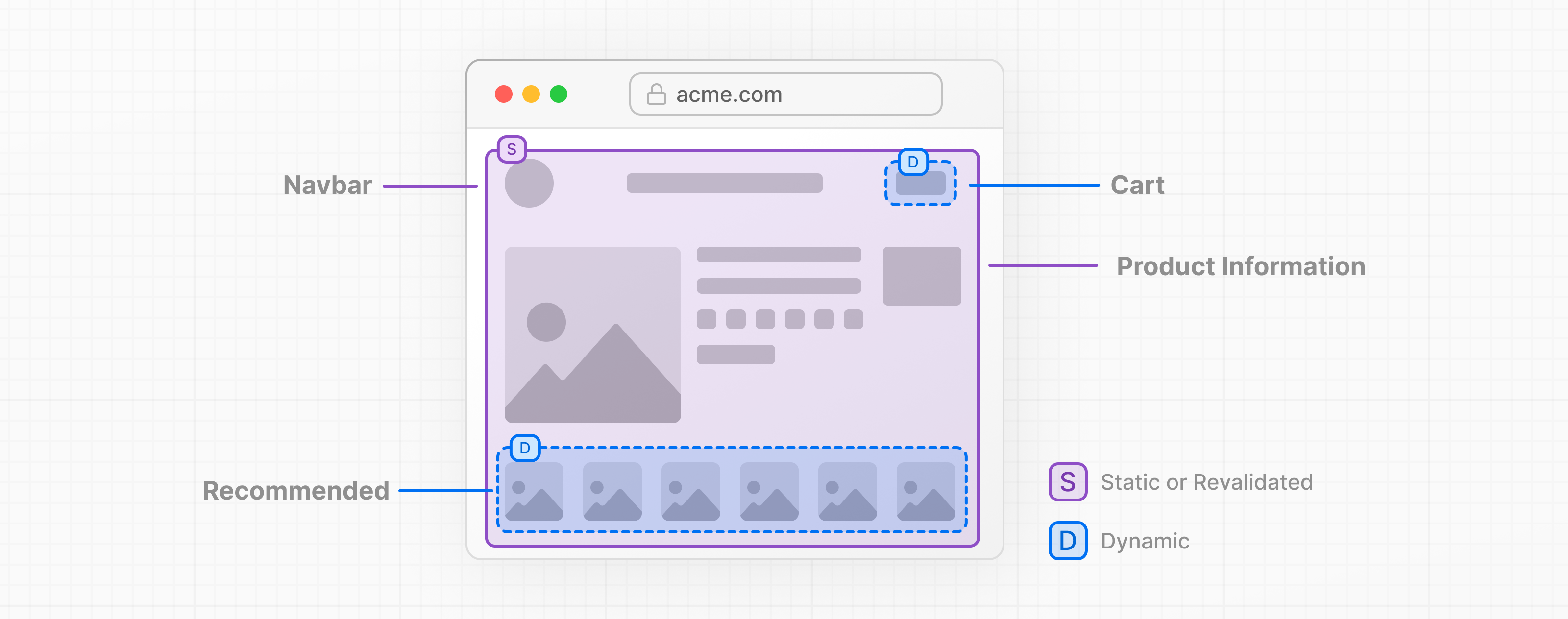
示例 4: 完整电商页面 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 import { Suspense } from "react" ;import { cacheLife, cacheTag } from "next/cache" ;import { cookies } from "next/headers" ;export default function ProductPage ({ params, }: { params: Promise <{ id: string }>; } ) { return ( <div > {/* 静态导航 - 立即显示 */} <nav > <a href ="/" > Home</a > <a href ="/products" > Products</a > </nav > {/* 产品信息 - 公共缓存,1 小时 */} <Suspense fallback ={ <ProductSkeleton /> }> <ProductInfo params ={params} /> </Suspense > {/* 用户购物车 - 动态,无缓存 */} <Suspense fallback ={ <CartSkeleton /> }> <UserCart /> </Suspense > {/* 推荐商品 - 公共缓存,1 天 */} <Suspense fallback ={ <RecommendationsSkeleton /> }> <Recommendations params ={params} /> </Suspense > </div > ); } async function ProductInfo ({ params }: { params: Promise <{ id: string }> } ) { "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); cacheTag ("products" ); const { id } = await params; const product = await db.products .findUnique ({ where : { id } }); return ( <div > <h1 > {product.name}</h1 > <p > {product.description}</p > <p > Price: ${product.price}</p > </div > ); } async function UserCart ( const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; const cart = await db.carts .findUnique ({ where : { userId }, include : { items : true }, }); return ( <div > <h2 > Your Cart</h2 > <p > {cart.items.length} items</p > </div > ); } async function Recommendations ({ params, }: { params: Promise <{ id: string }>; } ) { "use cache" ; cacheLife ("days" ); const { id } = await params; const recommendations = await getRecommendations (id); return ( <div > <h2 > You might also like</h2 > <ul > {recommendations.map((r) => ( <li key ={r.id} > {r.name}</li > ))} </ul > </div > ); }
最佳实践 1. 根据数据特性选择策略 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 async function getCategories ( "use cache" ; cacheLife ("days" ); cacheTag ("categories" ); return await db.categories .findMany (); } async function getUserProfile ( const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; return await db.users .findUnique ({ where : { id : userId } }); } async function getLiveData ( await connection (); return await fetch ("https://api.example.com/live" ); }
2. 合理使用 Suspense 嵌套 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 export default function Page ( return ( <div > {/* 外层:页面级 Suspense */} <Suspense fallback ={ <PageSkeleton /> }> <PageContent /> </Suspense > </div > ); } async function PageContent ( return ( <div > <StaticHeader /> {/* 内层:组件级 Suspense,细粒度控制 */} <Suspense fallback ={ <UserSkeleton /> }> <UserInfo /> </Suspense > <Suspense fallback ={ <ProductsSkeleton /> }> <ProductList /> </Suspense > </div > ); }
3. 缓存粒度策略 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 async function ProductCard ({ id }: { id: string } ) { "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); cacheTag ("products" , `product-${id} ` ); const product = await db.products .findUnique ({ where : { id } }); return <div > {product.name}</div > } export default function ProductList ({ ids }: { ids: string [] } ) { return ( <div > {ids.map((id) => ( <ProductCard key ={id} id ={id} /> ))} </div > ); } export default async function ProductList ({ ids }: { ids: string [] } ) { "use cache" ; const products = await db.products .findMany ({ where : { id : { in : ids } }, }); return ( <div > {products.map((p) => ( <div key ={p.id} > {p.name}</div > ))} </div > ); }
为什么细粒度更好 :
单个产品更新时,只需要使一个缓存失效
不同产品可以有不同的缓存策略
更容易调试和维护
4. 多级缓存标签 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 async function ProductDetails ({ id }: { id: string } ) { "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); cacheTag ( "products" , `product-${id} ` , `category-electronics` ); const product = await db.products .findUnique ({ where : { id } }); return <div > {product.name}</div > }
5. generateStaticParams 最佳实践 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 export async function generateStaticParams ( const topProducts = await db.products .orderBy ("views" , "desc" ) .limit (20 ) .select ("id" ); return topProducts.map ((p ) => ({ id : p.id })); } export default async function ProductPage ({ params, }: { params: Promise <{ id: string }>; } ) { "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); cacheTag ("products" ); const { id } = await params; const product = await db.products .findUnique ({ where : { id } }); return <div > {product.name}</div > }
策略说明 :
低基数参数 (如分类、语言):预生成所有值高基数参数 (如产品 ID):只预生成热门值按需生成 + 缓存 = ISR 效果
和 Next-intl 结合 现在使用 next-intl 可能会导致报各种缺少 Suspense 边界的错,这个的核心是在不指定 locale 的情况下,使用getTranslate,useTranslate,<Link>(next-intl 的 Link)会去读取 header(x-next-intl-locale),相当于这个库会自己去用 dynamic api。
要解决很简单,拿到 locale 之后塞到setRequestLocale里或者直接塞到各个的 locale 参数里。
这个和解决 static 渲染类似。
参考:Add setRequestLocale to all relevant layouts and pages
常见错误与解决方案 错误 1: 缺少 Suspense 边界 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 export default async function Page ( const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; return <div > {userId}</div > } export default function Page ( return ( <Suspense fallback ={ <Loading /> }> <UserContent /> </Suspense > ); } async function UserContent ( const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; return <div > {userId}</div > } export default async function Page ( "use cache" ; }
错误 2: 在 use cache 中使用运行时 API 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 async function Component ( "use cache" ; const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; return <div > {userId}</div > } async function Component ( const userId = (await cookies ()).get ("userId" )?.value ; return <div > {userId}</div > } export default function Page ( return ( <Suspense fallback ={ <Loading /> }> <Component /> </Suspense > ); }
错误 3: Route Segment Config 不兼容 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 export const revalidate = 60 ;export const dynamic = "force-static" ;import { cacheLife } from "next/cache" ;export default async function Page ( "use cache" ; cacheLife ({ revalidate : 60 }); }
错误 4: 未 await params/searchParams 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 export default function Page ({ params } ) { const id = params.id ; } export default async function Page ({ params, }: { params: Promise <{ id: string }>; } ) { const { id } = await params; return <div > Product: {id}</div > }
错误 5: 在 Route Handler 主体中使用 use cache 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 export async function GET ( "use cache" ; return Response .json ({ data : "..." }); } async function getData ( "use cache" ; cacheLife ("hours" ); return await db.query ("SELECT * FROM data" ); } export async function GET ( const data = await getData (); return Response .json (data); }
错误 6: 传递不可序列化的参数到 use cache 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 async function cachedFunction (callback : () => void "use cache" ; callback (); } async function cachedWrapper ({ children }: { children: ReactNode } ) { "use cache" ; return <div > {children}</div > } async function cachedFunction (data : { id: number ; name: string } "use cache" ; return data; }
FAQ Q: Cache Components 是否取代 PPR? A : 不。Cache Components 实现了 PPR 作为特性。旧的实验性 PPR 标志已被移除,但 PPR 仍然存在。
PPR 提供静态外壳和流式传输基础设施use cache
Q: 我应该首先缓存什么? A : 你缓存的内容应该取决于你希望 UI 加载状态是什么。如果数据不依赖运行时数据,并且你可以接受在一段时间内为多个请求提供缓存值,请使用 use cache 和 cacheLife 来描述该行为。
对于具有更新机制的内容管理系统,考虑使用具有较长缓存持续时间的标签,并依赖 revalidateTag 将静态初始 UI 标记为准备重新验证。这种模式允许你提供快速、缓存的响应,同时在内容实际更改时仍然更新内容,而不是提前过期缓存。
Q: 如何快速更新缓存内容? A : 使用 cacheTagupdateTagrevalidateTag
选择指南 :
场景
使用
行为
需要立即看到更新
updateTag立即过期,同一请求内刷新
可以容忍短暂过期
revalidateTagStale-while-revalidate,后台更新
Q: ISR 还支持吗? A : 是的,ISR 功能仍然存在,但 API 已更改:
❌ export const revalidate = 60
✅ cacheLife({ revalidate: 60 })
使用 use cache + cacheLife + generateStaticParams 可以实现完整的 ISR 功能。
Q: 可以混用旧 API 和新 API 吗? A : 不可以。启用 cacheComponents: true 后:
❌ 不能使用 export const revalidate
❌ 不能使用 export const dynamic
❌ 不能使用 export const fetchCache
✅ 必须使用 use cache + cacheLife
Q: Edge Runtime 支持吗? A : 不支持。Cache Components 需要 Node.js 运行时。
参考资料 官方文档
关键 API 速查 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 "use cache" ;import { cacheLife, cacheTag } from "next/cache" ;cacheLife ("hours" );cacheLife ({ stale : 60 , revalidate : 300 , expire : 3600 });cacheTag ("tag1" , "tag2" );import { updateTag, revalidateTag } from "next/cache" ;updateTag ("tag" ); revalidateTag ("tag" , "max" ); import { cookies, headers } from "next/headers" ;import { connection } from "next/server" ;await cookies ();await headers ();await connection ();import { Suspense } from "react" ;<Suspense fallback ={ <Loading /> }> <DynamicComponent /> </Suspense >
视频资源
总结 Cache Components 的核心理念 :
Cache Components = PPR + use cache
PPR 是基础(静态外壳 + 流式传输)
use cache 是增强(显式缓存控制)
默认动态,选择性缓存
与旧版本相反,现在默认都是动态的
你决定什么需要缓存
三个关键工具
Suspense for runtime data(运行时数据)
Suspense for dynamic data(动态数据)
use cache for cached data(缓存数据)
从旧 API 迁移
移除所有 Route Segment Config
使用 use cache + cacheLife 替代
params/searchParams 现在是 Promise(你从 Next.js 15 来的这点就问题不大)
最佳实践
根据数据特性选择策略
细粒度缓存优于粗粒度
合理使用 Suspense 嵌套
多级缓存标签便于失效管理
Cache Components 让缓存行为更清晰、更可控,是构建高性能 Next.js 应用的强大工具。